In this mass of about 1.5 kg dwell some 86 billion neurons that make up the gray matter. This is roughly equal to the number of stars in the Milky Way.
These neurons are connected to each other by means of Synapsis. It is estimated that the number of synapses in the human brain is close to one quadrillion, i.e. 1 followed by 15 zeros.
Scientists know these connections exist, but they still can’t figure out how and where all the information arriving and leaving our brains is produced, stored and processed thanks to those synapses.
An example of such puzzles for the brain and memory is the so-called “uncertain territory”an area around which there are more questions than answers.
This part of the brain was first described by the Swiss neuroanatomist Auguste Henri Forel in 1877.
“It’s an area we can’t say for sure nothing is certainForell Books.
Illustration of a synapse between two neurons.
Today, nearly 150 years later, it’s still more or less the same. Despite all the advances in medicine and technology, no one really understands what the uncharted territory is.
Amidst the uncertainty, however, experts have evidence that the region of uncertainty plays a role in key processes in the human body such as memory.
However, it is a part that has been little studied.
But recent studies have found new clues to this important but neglected region of our brain.
certainty (little)
The uncertainty zone is also known as the uncertainty zone.
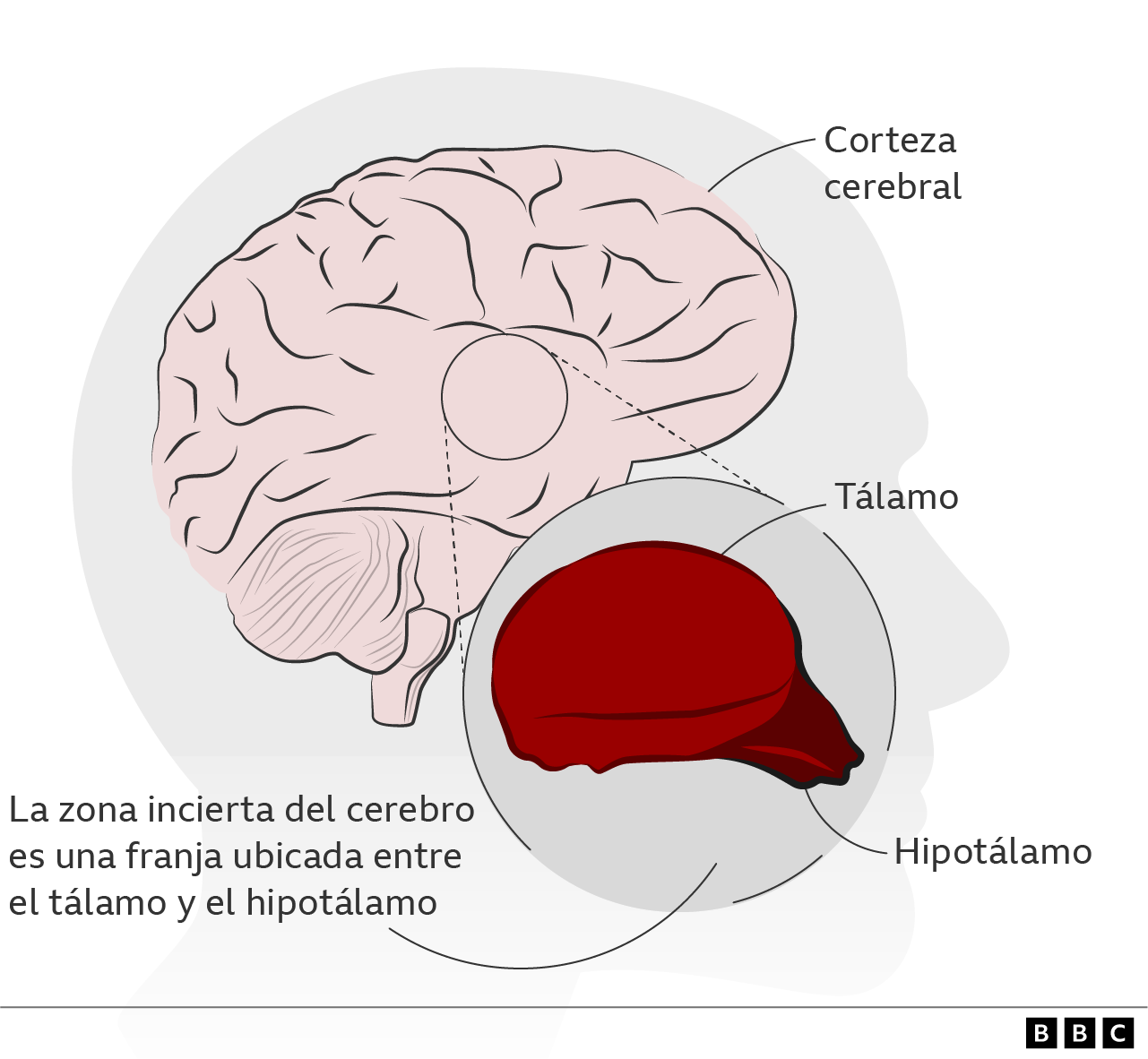
This area is A band of gray matter It is located in the central region of the brain.
“he looks like A sheet of neurons that extend between the thalamus and the hypothalamus,” Dr Huizhong Tao, professor of physiology and neurosciences at USC, told BBC Mundo.
BBC
Throughout the necrotic region, at least four subregions have been identified, each associated with a specific role, ranging from motor and visceral functions to Excitement and interest.
The volatile area has also been linked to functions such as sleep, Pain regulation And learning, as Dr. Huizhong explains.
And a recent study in rats showed that it can also play an important role in promoting metabolism long term memory
Moreover, little is known about the mechanisms by which W How do you communicate with other brain regions to accomplish their tasks.
For example, the uncertain area is one of the few areas commonly targeted for stimulation Parkinson’s patientsBut scientists aren’t sure why it can relieve symptoms of the disease.
Why is it difficult to study?
The uncertain region is a thin structure located at deep in the brainso it is difficult to study them in living people, says Huizhong.
In addition, the expert explains the chemical and cellular composition of This membrane is complex.
Each of its subdivisions appears to have different functions, and its neurons involve the action of as many as 20 different neurotransmitters, making it Difficult to analyze as a whole.
And as if that weren’t enough, “its connection to other parts of the brain is too complicatedHuizhong says.
The unpaired region communicates with nearly every center of the neural circuits, from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord, which also helps explain why it is involved in such diverse roles.
What clues have emerged?
A recent study in mice, conducted by the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in Germany, found new evidence that the non-brain region may play a key role in brain function. Attention span and permanent memory.
The analysis showed that the unstressed area has a special connection with the neocortex, area Bigger and more developed from the brain.
In humans, it is considered the neocortex Storage increase of long term memories. It is also responsible for many of the cognitive functions that characterize us, such as thinking, awareness, and language.
However, it is not known exactly how Memories and experiences They pray and stay there.
The uncertain zone plays a role in consolidating memory.
internal and external signals
To form new memories, the brain must associate sensory stimuli coming from the outside with internal signals They contain information from past experiences.
To do this, neurons exchange signals excite (activate) or inhibit (deactivate) Certain regions of the brain as needed.
In the past, studies focused on looking at the effect of excitation signals in learning and memory.
This new study, by contrast, focused on inhibitory signals that arise from the uncertain region.
In this way, they note that the uncertain region plays a role in Learning and memorynot by excitation of other neurons, but by inhibition.
The unstressed area acts like a network of traffic lights that improves the movement of signals in the brain.
This inhibition from the uncertain region creates a “inhibiting network” which disrupts some connections to improve the flow of erotic connections in others.
This “inhibitory network” can be compared to a traffic signal system Which coordinate with each other to stop traffic on some roads and thus allow it to flow faster on other roads.
What we noticed was Complete redistribution of inhibition within the system,” says Anna Schroeder, lead author of the study.
Through this mechanism, the end result is the excitation of circuits in the neocortex to facilitate learning.
because it is important?
“This study is very interesting,” says Dr. Huizhong, who was not involved in the research.
“It provides new insights into the neural mechanisms of learning and memory.”
The research’s authors stress that understanding the mechanisms by which memories are formed can be useful in treatments for amnesia, Anxiety disorders or Parkinson’s disease.
They even state that it may have implications for development artificial intelligence and software development.
However, they are currently satisfied with the usefulness of their studies “Inspire other researchers” To continue searching for clues to solve the mystery of the uncertain area.

“Beeraholic. Friend of animals everywhere. Evil web scholar. Zombie maven.”

:quality(85)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/infobae/7GTZZ3YRERFV7J75VEPMTMDSHU.jpg)



:quality(85)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/infobae/TPKDIBIMCFGHVFKHL54I4F4ICM.jpg)






More Stories
A valve failure led to the cancellation of the first manned test of the Boeing Starliner two hours before launch
Gustavo Pietro and his harsh warning: “First they overthrow the president instead of privatizing health”
What is Euler number (e) and what is it used for?